前言
本月继续对 Flutter CoderWhy 视频教程 学习做个笔记~ 惯例还是会提几个 question 思考?🤔
Flutter 两种风格
Flutter 设计两种风格 App :Material Design 风格 MaterialApp 和 iOS 风格的 CupertinoApp
Scaffold
Scaffold 脚手架:主要用来定义页面的基础结构,比如上导航、内容区域、下导航、侧边栏
- 有相关属性:appbar、drawer、body
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
main() {
// runApp 函数
runApp(MaterialApp(
// debugShowCheckedModeBanner: false, // 控制界面右上角是否显示`debug`提示
home: Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text("第一个Flutter程序"),
),
body: Center(
child: Text(
"Hello World",
textDirection: TextDirection.ltr,
style: TextStyle(fontSize: 30, color: Colors.orange),
),
),
),
));
}Widget
Flutter 中万物皆Widget (组件/部件)
Widget 有两种:StatelessWidget && StatefulWidget
StatelessWidget
没有状态改变的 Widget,通常是做一些展示工作
为什么 StatelessWidget 是不可以变的?
- StatelessWidget 继承至 Widget
- Widget 是 @immutable 修饰的,不可以变的。所以 StatelessWidget 是不可变的
- @immutable: 注解标明的类或者子类都必须是不可变的 传送门
- 所以 Widget 定义的成员变量必须使用 final 定义
- 题外话(注解应用):Flutter 注解处理及代码生成
- 继承 StatelessWidget 子类,必须要实现
Widget build(BuildContext context)抽象方法
StatelessWidget & Widget 的源码
abstract class Widget extends DiagnosticableTree {
// ...
}
abstract class StatelessWidget extends Widget {
/// Initializes [key] for subclasses.
const StatelessWidget({ Key key }) : super(key: key);
/// Creates a [StatelessElement] to manage this widget's location in the tree.
///
/// It is uncommon for subclasses to override this method.
StatelessElement createElement() => StatelessElement(this);
Widget build(BuildContext context);
}生命周期
先调用 构造函数,再调用 build
class ZQLifeCycleStatelessWidget extends StatelessWidget {
final String message;
ZQLifeCycleStatelessWidget(this.message) {
print("构造函数被调用");
}
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
print("调用build方法");
return Text(this.message);
}
}StatefulWidget
有状态改变的 Widget, 通常做交互变化状态,或者页面依据 data 刷新展示
为什么 StatefullWidget 是可变的?
- 📢 其实无论 StatelessWidget 还是 StatefulWidget,其父类都是 Widget 因此它定义成员变量也是 final 修饰不可变~
- 但是继承 StatefulWidget 的子类,必需要实现
State createState();抽像方法。- 所以可以变的是 State 这也是与 StatelessWidget 不一样的地方
StatefulWidget 的源码
abstract class StatefulWidget extends Widget {
/// Initializes [key] for subclasses.
const StatefulWidget({ Key key }) : super(key: key);
/// Creates a [StatefulElement] to manage this widget's location in the tree.
///
/// It is uncommon for subclasses to override this method.
StatefulElement createElement() => StatefulElement(this);
/// Creates the mutable state for this widget at a given location in the tree.
///
/// Subclasses should override this method to return a newly created
/// instance of their associated [State] subclass:
///
/// ```dart
/// @override
/// _MyState createState() => _MyState();
/// ```
///
/// The framework can call this method multiple times over the lifetime of
/// a [StatefulWidget]. For example, if the widget is inserted into the tree
/// in multiple locations, the framework will create a separate [State] object
/// for each location. Similarly, if the widget is removed from the tree and
/// later inserted into the tree again, the framework will call [createState]
/// again to create a fresh [State] object, simplifying the lifecycle of
/// [State] objects.
State createState();
}State 的源码
abstract class State<T extends StatefulWidget> with Diagnosticable {
// ...
/// an argument.
T get widget => _widget;
T _widget;
_StateLifecycle _debugLifecycleState = _StateLifecycle.created;
BuildContext get context => _element;
StatefulElement _element;
bool get mounted => _element != null;
void initState() {
assert(_debugLifecycleState == _StateLifecycle.created);
}
void didUpdateWidget(covariant T oldWidget) { }
void reassemble() { }
void setState(VoidCallback fn) {
assert(fn != null);
assert(() {
if (_debugLifecycleState == _StateLifecycle.defunct) {
throw FlutterError.fromParts(<DiagnosticsNode>[
ErrorSummary('setState() called after dispose(): $this'),
ErrorDescription(
'This error happens if you call setState() on a State object for a widget that '
'no longer appears in the widget tree (e.g., whose parent widget no longer '
'includes the widget in its build). This error can occur when code calls '
'setState() from a timer or an animation callback.'
),
ErrorHint(
'The preferred solution is '
'to cancel the timer or stop listening to the animation in the dispose() '
'callback. Another solution is to check the "mounted" property of this '
'object before calling setState() to ensure the object is still in the '
'tree.'
),
ErrorHint(
'This error might indicate a memory leak if setState() is being called '
'because another object is retaining a reference to this State object '
'after it has been removed from the tree. To avoid memory leaks, '
'consider breaking the reference to this object during dispose().'
),
]);
}
if (_debugLifecycleState == _StateLifecycle.created && !mounted) {
throw FlutterError.fromParts(<DiagnosticsNode>[
ErrorSummary('setState() called in constructor: $this'),
ErrorHint(
'This happens when you call setState() on a State object for a widget that '
"hasn't been inserted into the widget tree yet. It is not necessary to call "
'setState() in the constructor, since the state is already assumed to be dirty '
'when it is initially created.'
),
]);
}
return true;
}());
final dynamic result = fn() as dynamic;
assert(() {
if (result is Future) {
throw FlutterError.fromParts(<DiagnosticsNode>[
ErrorSummary('setState() callback argument returned a Future.'),
ErrorDescription(
'The setState() method on $this was called with a closure or method that '
'returned a Future. Maybe it is marked as "async".'
),
ErrorHint(
'Instead of performing asynchronous work inside a call to setState(), first '
'execute the work (without updating the widget state), and then synchronously '
'update the state inside a call to setState().'
),
]);
}
// We ignore other types of return values so that you can do things like:
// setState(() => x = 3);
return true;
}());
_element.markNeedsBuild();
}
void deactivate() { }
void dispose() {
assert(_debugLifecycleState == _StateLifecycle.ready);
assert(() {
_debugLifecycleState = _StateLifecycle.defunct;
return true;
}());
}
Widget build(BuildContext context);
void didChangeDependencies() { }
// ..
}question
我们都知道在 StatefullWidget 中更新数据想让界面变化需要调用 setState,这是为什么呢?
setState 涉及的源码
void markNeedsBuild() {
assert(_debugLifecycleState != _ElementLifecycle.defunct);
if (!_active)
return;
// ...
if (dirty)
return;
_dirty = true;
owner.scheduleBuildFor(this);
}
void scheduleBuildFor(Element element) {
...
if (!_scheduledFlushDirtyElements && onBuildScheduled != null) {
_scheduledFlushDirtyElements = true;
onBuildScheduled();
}
_dirtyElements.add(element);
element._inDirtyList = true;
// ...
}
void scheduleFrame() {
if (_hasScheduledFrame || !_framesEnabled)
return;
assert(() {
if (debugPrintScheduleFrameStacks)
debugPrintStack(label: 'scheduleFrame() called. Current phase is $schedulerPhase.');
return true;
}());
window.scheduleFrame();
_hasScheduledFrame = true;
}
void _handleBuildScheduled() {
//调用ensureVisualUpdate
ensureVisualUpdate();
}
void ensureVisualUpdate() {
switch (schedulerPhase) {
case SchedulerPhase.idle:
case SchedulerPhase.postFrameCallbacks:
//当schedulerPhase为SchedulerPhase.idle,
//SchedulerPhase.postFrameCallbacks时调用scheduleFrame()
scheduleFrame();
return;
case SchedulerPhase.transientCallbacks:
case SchedulerPhase.midFrameMicrotasks:
case SchedulerPhase.persistentCallbacks:
return;
}
}所以对上面源码我做了总结:
- 从源码看出 StatefullWidget 需要实现 createState 方法,而 State 的子类是可以是存储状态变量的,所以可以看出其与 StatelessWidget 区别
- 对上述问题:StatefullWidget 调用 setState 原因~
- 因为调用
setState调用过程markNeedsBuild=>onBuildScheduled=>scheduleFrame=>drawFrame(具体参看 Flutter的setState更新原理和流程) - UI 线程的绘制过程的核心是执行 WidgetsBinding 的
drawFrame方法,然后会创建layer tree视图树
- 因为调用
生命周期
class ZQLifeCycleStatefullWidget extends StatefulWidget {
ZQLifeCycleStatefullWidget() {
print("1.调用 ZQLifeCycleStatefullWidget 的 constructor 方法");
}
_ZQLifeCycleStatefullWidgetState createState() {
print("2.调用 ZQLifeCycleStatefullWidget 的 createState 方法");
return _ZQLifeCycleStatefullWidgetState();
}
}
class _ZQLifeCycleStatefullWidgetState extends State<ZQLifeCycleStatefullWidget> {
_ZQLifeCycleStatefullWidgetState() {
print("3. 调用 ZQLifeCycleStatefullWidgetState 的 constructor 方法");
}
void initState() {
// TODO: implement initState 📢 这里必须调用 super(@mustCallSuper)
super.initState();
print("4. 调用 ZQLifeCycleStatefullWidgetState 的 initState 方法");
}
void didChangeDependencies() {
super.didChangeDependencies();
print("调用 ZQLifeCycleStatefullWidgetState 的 didChangeDependencies 方法");
}
void didUpdateWidget(covariant ZQLifeCycleStatefullWidget oldWidget) {
// TODO: implement didUpdateWidget
super.didUpdateWidget(oldWidget);
print("调用 ZQLifeCycleStatefullWidgetState 的 didUpdateWidget 方法");
}
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
print("5. 调用 ZQLifeCycleStatefullWidgetState 的 build 方法");
return Text("ZQLifeCycleStatefullWidgetState");
}
void dispose() {
super.dispose();
print("6. 调用 ZQLifeCycleStatefullWidgetState 的 dispose 方法");
}
}flutter: 1.调用 ZQLifeCycleStatefullWidget 的 constructor 方法
flutter: 2.调用 ZQLifeCycleStatefullWidget 的 createState 方法
flutter: 3. 调用 ZQLifeCycleStatefullWidgetState 的 constructor 方法
flutter: 4. 调用 ZQLifeCycleStatefullWidgetState 的 initState 方法
flutter: 调用 ZQLifeCycleStatefullWidgetState 的 didChangeDependencies 方法
flutter: 5. 调用 ZQLifeCycleStatefullWidgetState 的 build 方法
>>>> 点击计数按钮
flutter: 1.调用 ZQLifeCycleStatefullWidget 的 constructor 方法
flutter: 调用 ZQLifeCycleStatefullWidgetState 的 didUpdateWidget 方法
flutter: 5. 调用 ZQLifeCycleStatefullWidgetState 的 build 方法流程图
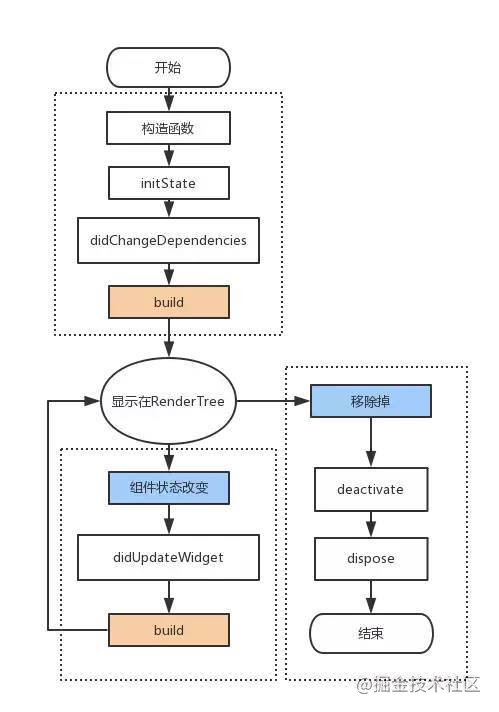
依次触发顺序
- createState
- 初始化构造时候会触发
- initState
- 注意:在 override initState 的时候必须要调用 super.initState():
- 类似 iOS viewDidLoad
- 此时 mount 为true
- didChangeDependencies
- 调用initState会调用;
- 从其他对象中依赖一些数据发生改变时,比如 InheritedWidget
- build
- addPostFrameCallback
- didUpdateWidget
- 执行 didUpdateWidget 方法是在当父Widget触发重建(rebuild)时,系统会调用 didUpdateWidget 方法
- deactivate
- dispose
question
为什么在 override initState 的时候必须要调用 super.initState():?
- 原因是: @mustCallSuper 注解作用,要求子类必需调用父类方法
方法说明
摘抄至: 传送门
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| createState | Framework 会通过调用StatefulWidget.createState 来创建一个 State。 |
| initState | 新创建的 State 会和一个 BuildContext 产生关联,此时认为 State 已经被安装好了,initState 函数将会被调用。通常,我们可以重写这个函数,进行初始化操作。 |
| didChangeDependencies | 在 initState 调用结束后,这个函数会被调用。事实上,当 State 对象的依赖关系发生变化时,这个函数总会被 Framework 调用。 |
| build | 经过以上步骤,系统认为一个 State 已经准备好了,就会调用 build 来构建视图。我们需要在这个函数中返回一个 Widget。 |
| deactivate | deactivate 当 State 被暂时从视图树中移除时,会调用这个函数。页面切换时,也会调用它,因为此时 State 在视图树中的位置发生了变化,需要先暂时移除后添加。 |
| dispose | 当 State 被永久地从视图树中移除时,Framework 会调用该函数。在销毁前触发,我们可以在这里进行最终的资源释放。在调用这个函数之前,总会先调用 deactivate 函数。 |
| didUpdateWidget | 当 Widget 的配置发生变化时,会调用这个函数。比如,热重载的时候就会调用这个函数。调用这个函数后,会调用 build 函数。 |
| setState | 当需要更新 State 的视图时,需要手动调用这个函数,它会触发 build 函数。 |
StatefulWidget & State 流程关系图
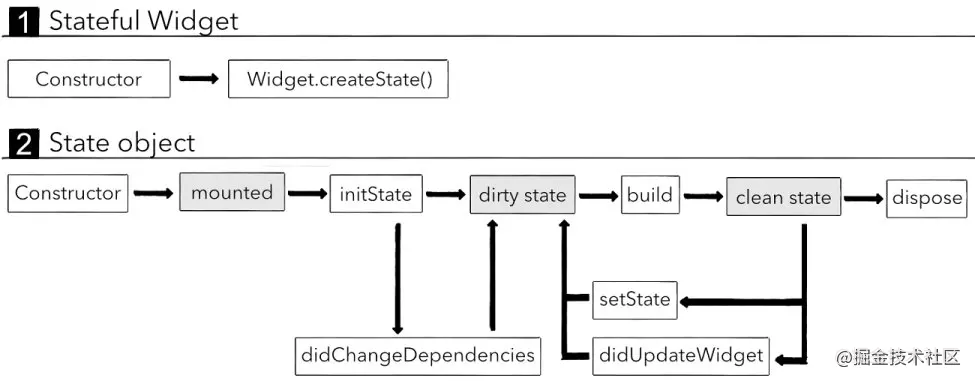
quesion
在 setState 中 mounted 的作用是?
总结:
- StatelessWidget 是不可变的而 StatefullWidget 的状态是可变的,主要原因是是和其重写的抽象方法有关
- StatelessWidget:
Widget build(BuildContext context) - StatefullWidget:
State createState()
- StatelessWidget:
- widget 最终渲染的东西是什么看的是 build 方法里返回的是什么,比如有的返回是
RenderObjectWidget如果是 StatefullWidget 的看的是 state 返回的 build
快捷键
- 输入
stl或stful快捷键快速创建 widget alt+enter包裹组件option+enter将 StatelessWidget 转 StatefullWidgetoption+enter+w抽成 widgetcommand+alt+b查看抽象类的实现类
声明式编程 & 命令式编程
- 命令式编程的主要思想是关注执行的步骤,即一步一步告诉计算机先做什么再做什么
- 声明式编程是以数据结构的形式来表达程序执行的逻辑。应该做什么,但不指定具体要怎么做
代码示例
参考
Thanks
若没有本文 Issue,您可以使用 Comment 模版新建。
GitHub Issues